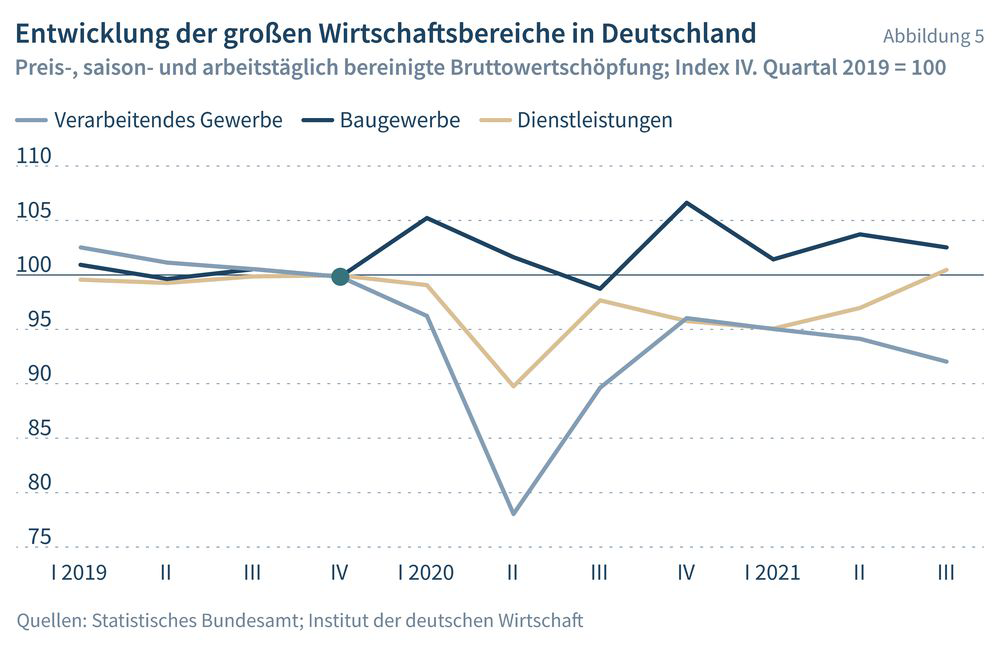
In the course of 2021 Germany’s economic recovery has once again perceptibly lost momentum. After the strain brought about at the beginning of the year by the lockdown for the second and third waves of the Covid19 pandemic, manufacturing and construction companies are now struggling with a shortage of materials, while higher prices for fossil fuels are imposing an additional burden.

IW Economic Forecast Winter 2021: Disrupted Production, Price Rises and Pandemic Policies

In the course of 2021 Germany’s economic recovery has once again perceptibly lost momentum. After the strain brought about at the beginning of the year by the lockdown for the second and third waves of the Covid19 pandemic, manufacturing and construction companies are now struggling with a shortage of materials, while higher prices for fossil fuels are imposing an additional burden.
These factors are also hobbling global growth. Due to the sharp increase in production costs, consumer prices are now rising sharply, thus slowing the recovery in consumption. The steep upturn in infection rates in Germany since October 2021 will trigger a renewed slowdown in consumption and the relevant sectors of the economy in the 2021/2022 winter. The combined influence of disrupted production, rising prices and Covid19 regulations will further delay the return to economic normality. After growing by only 2 ½ per cent in 2021, the German economy will expand by just under 4 per cent in 2022. This is based on the assumption that, despite ongoing bottlenecks in some areas, the majority of the current disruptions to production will ease in the course of the year, thus also reducing inflationary pressures. The negative effects of the pandemic on the German labour market will be largely overcome in 2022. Employment will actually exceed pre-crisis levels, while at just under 2.4 million the number of unemployed will also be slightly higher. The unemployment rate will fall to 5 ¼ per cent. After the massive charges on government financing in 2020 and 2021, next year’s budget deficit will decline to 2 per cent of GDP and the government debt ratio will revert to a level of 70 per cent.

IW Economic Forecast Winter 2021: Disrupted Production, Price Rises and Pandemic Policies

More on the topic

Determinants of personnel planning in Germany
The German labor market has been growing since 2005. The dip in the wake of the coronavirus pandemic between 2020 and 2022 is an exception, as the German labor market has reached a record level of 45.9 million people in employment by 2023.
IW
Effects of the Middle East conflict on the German economy
Beyond the humanitarian crisis associated with the geopolitical conflict in Israel, which affects millions of human lives, the Middle East conflict also leaves lasting marks on economic activity not only in the affected region, but also in Germany and the ...
IW